|
About this Database
Malaria
Full-Length cDNA project
1-2.Malaria cDNA Project
1-2-1.
Complex Life Cycle of Malaria Parasite
The life of
the plasmodium passes in two hosts, a vertebrate and a mosquito. When ana
infected female Anopheles mosquito bites a human, infective sporozoites
are injected into the human bloodstream.
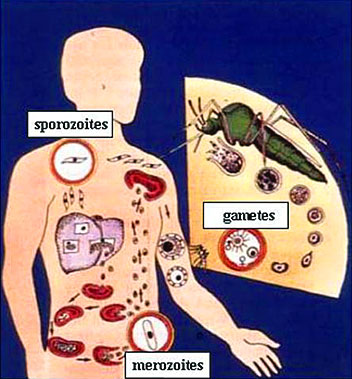 |
Within 30 minutes these slender-form parasites invade the human hepatocytes,
where they start multiplication and produce thousands of merozoites within
a week (exoerythocytic schizogony). When the multinucleate schizont
ruptures, the released merozoites enter red blood cells, in which they undergo
a second phase of multiplication (erythrocytic schizogony) and form
about 20 merozoites. They can infect new red blood cells and this process
can be repeated many times. Some merozoites develop into sexual-stage gametocytes,
i.e., female macrogametocytes and male microgametocytes. These are taken
up by a mosquito. In the midgut, a microgametocyte undergoes a process of
maturation that results in the production of eight sperm-like microgametes
(exflagellation). They fertilize a mature macrogamete, forming a
zygote. The zygote becomes elongated and active and is called an ookinete.
The ookinete penetrates the gut wall and comes to lie on the outer surface
of the gut but beneath the outer covering of that organ, where it forms
an oocyst. The oocysts grow and produce thousands of sporozoites (sporogony).
With the rupture of the oocysts, sporozoites are liberated into the body
cavity and migrate to the salivary glands, where they wait until a second
bite starts the infection cycle again.
|
- Background
- Construction
of Malaria Full-Length cDNA Library
- Current
Status
- Experimental
Procedures
|